Juana Valle never imagined she’d be scared to drink water from her tap or eat fresh eggs and walnuts when she bought her 5-acre farm in San Juan Bautista, California, three years ago. Escaping city life and growing her own food was a dream come true for the 52-year-old.
Then Valle began to suspect water from her well was making her sick.
“Even if everything is organic, it doesn’t matter, if the water underground is not clean,” Valle said.
This year, researchers found worrisome levels of chemicals called PFAS in her well water. Exposure to PFAS, a group of thousands of compounds, has been linked to health problems including cancer, decreased response to vaccines, and low birth weight, according to a federally funded report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Valle worries that eating food from her farm and drinking the water, found also to contain arsenic, are to blame for health issues she’s experienced recently.
The researchers suspect the toxic chemicals could have made their way into Valle’s water through nearby agricultural operations, which may have used PFAS-laced fertilizers made from dried sludge from wastewater treatment plants, or pesticides found to contain the compounds.
The chemicals have unexpectedly turned up in well water in rural farmland far from known contamination sites, like industrial areas, airports, and military bases. Agricultural communities already face the dangers of heavy metals and nitrates contaminating their tap water. Now researchers worry that PFAS could further harm farmworkers and communities of color disproportionately. They have called for more testing.
“It seems like it’s an even more widespread problem than we realized,” said Clare Pace, a researcher at the University of California-Berkeley who is examining possible exposure from PFAS-contaminated pesticides.

Stubborn Sludge
Concerns are mounting nationwide about PFAS contamination transferred through the common practice of spreading solid waste from sewage treatment across farm fields. Officials in Maine outlawed spreading “biosolids,” as some sewage byproducts are called, on farms and other land in 2022. A study published in August found higher levels of PFAS in the blood of people in Maine who drank water from wells next to farms where biosolids were spread.
Contamination in sewage mostly comes from industrial discharges. But household sludge also contains PFAS because the chemicals are prevalent in personal care products and other commonly used items, said Sarah Alexander, executive director of the Maine Organic Farmers and Gardeners Association.
“We found that farms that were spread with sludge in the ’80s are still contaminated today,” Alexander said.
The first PFAS, or perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, were invented in the 1940s to prevent stains and sticking in household products. Today, PFAS chemicals are used in anything from cookware to cosmetics to some types of firefighting foam — ending up in landfills and wastewater treatment plants. Known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down in the environment, PFAS are so toxic that in water they are measured in parts per trillion, equivalent to one drop in 20 Olympic-size swimming pools. The chemicals accumulate in the human body.
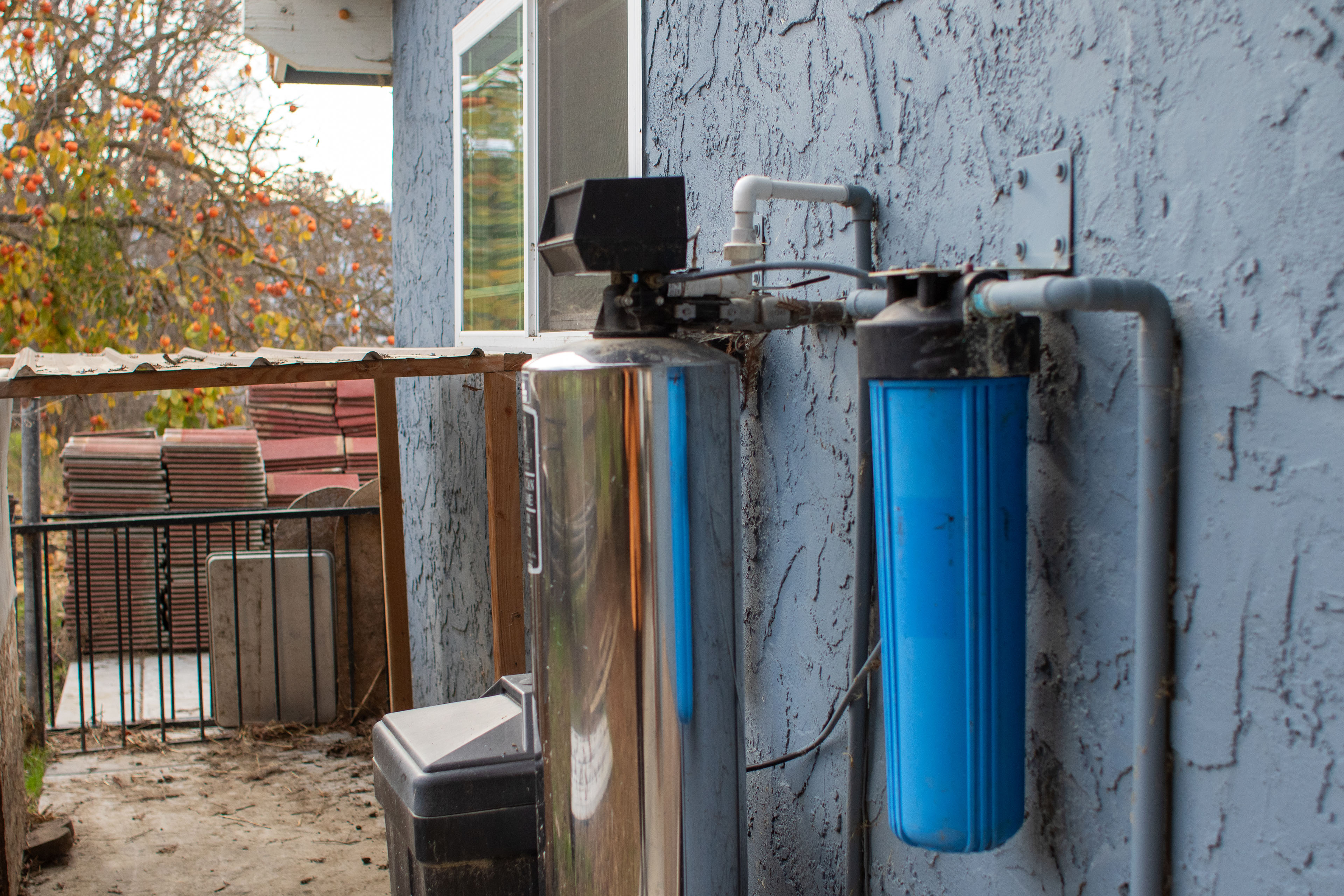
On Valle’s farm, her well water has PFAS concentrations eight times as high as the safety threshold the Environmental Protection Agency set this year for the PFAS chemical referred to as PFOS, or perfluorooctane sulfonate. It’s unclear whether the new drinking water standards, which are in a five-year implementation phase, will be enforced by the incoming Trump administration.


Valle’s well is one of 20 sites tested in California’s San Joaquin Valley and Central Coast regions — 10 private domestic wells and 10 public water systems — in the first round of preliminary sampling by UC-Berkeley researchers and the Community Water Center, a clean-water nonprofit. They’re planning community meetings to discuss the findings with residents when the results are finalized. Valle’s results showed 96 parts per trillion of total PFAS in her water, including 32 ppt of PFOS — both considered potentially hazardous amounts.
Hailey Shingler, who was part of the team that conducted the water sampling, said the sites’ proximity to farmland suggests agricultural operations could be a contamination source, or that the chemicals have become ubiquitous in the environment.
The EPA requires public water systems serving at least 3,300 people to test for 29 types of PFAS. But private wells are unregulated and particularly vulnerable to contamination from groundwater because they tend to be shallower and construction quality varies, Shingler said.
A Strain on the Water Supply
California already faces a drinking water crisis that disproportionately hits farmworkers and communities of color. More than 825,000 people spanning almost 400 water systems across the state don’t have access to clean or reliable drinking water because of contamination from nitrates, heavy metals, and pesticides.
California’s Central Valley is one of the nation’s biggest agricultural producers. State data shows the EPA found PFAS contamination above the new safety threshold in public drinking water supplies in some cities there: Fresno, Lathrop, Manteca, and others.
Not long after she moved, Valle started feeling sick. Joints in her legs hurt, and there was a burning sensation. Medical tests revealed her blood had high levels of heavy metals, especially arsenic, she said. She plans to get herself tested for PFAS soon, too.
“So I stopped eating [or drinking] anything from the farm,” Valle said, “and a week later my numbers went down.”
After that, she got a water filter installed for her house, but the system doesn’t remove PFAS, so she and her family continue to drink bottled water, she said.


In recent years, the pesticide industry has increased its use of PFAS for both active and “inert” ingredients, said David Andrews, a senior scientist of the Environmental Working Group, who analyzed pesticide ingredient registrations submitted to the EPA over the past decade as part of a recently published study.
“PFAS not only endanger agricultural workers and communities,” Andrews said, “but also jeopardize downstream water sources, where pesticide runoff can contaminate drinking supplies.”
California’s most concentrated pesticide use is along the Central Coast, where Valle lives, and in the Central Valley, said Pace, whose research found that possible PFAS contamination from pesticides disproportionately affects communities of color.
“Our results indicate racial and ethnic disparities in potential PFAS threats to community water systems, thus raising environmental justice concerns,” the paper states.
Spotty Solutions
Some treatment plants and public water systems have installed filtration systems to catch PFAS, but that can cost millions or even billions of dollars. California Gov. Gavin Newsom, a Democrat, signed laws restricting PFAS in textiles, food packaging, and cosmetics, a move the wastewater treatment industry hopes will address the problem at the source.
Yet the state, like the EPA, does not regulate PFAS in the solid waste generated by sewage treatment plants, though it does require monitoring.
In the past, biosolids were routinely sent to landfills alongside being spread on land. But in 2016, California lawmakers passed a regulation that requested operators to lower their organic waste disposal by 75% by 2025 to reduce methane emissions. That squeeze pushed facilities to repurpose more of their wastewater treatment byproducts as fertilizer, compost, and soil topper on farm fields, forests, and other sites.
Greg Kester, director of renewable resource programs at the California Association of Sanitation Agencies, said there are benefits to using biosolids as fertilizer, including improved soil health, increased crop yields, reduced irrigation needs, and carbon sequestration. “We have to look at the risk of not applying [it on farmland] as well,” he said.
Almost two-thirds of the 776,000 dry metric tons of biosolids California used or disposed of last year was spread this way, most of it hauled from wealthy, populated regions like Los Angeles County and the Bay Area to the Central Valley or out of state.
When asked if California would consider banning biosolids from agricultural use, Wendy Linck, a senior engineering geologist at California’s State Water Resources Control Board, said: “I don’t think that is in the future.”


Average PFAS concentrations found in California’s sampling of biosolids for PFAS collected by wastewater treatment plants are relatively low compared with more industrialized states like Maine, said Rashi Gupta, wastewater practice director at consulting firm Carollo Engineers.
Still, according to monitoring done in 2020 and 2022, San Francisco’s two wastewater treatment facilities produced biosolid samples with total PFAS levels of more than 150 parts per billion.
Starting in 2019, the water board began testing wells — and finding high levels of PFAS — near known sites of contamination, like airports, landfills, and industry.
The agency is now testing roughly 4,000 wells statewide, including those far from known contamination sources — free of charge in disadvantaged communities, according to Dan Newton, assistant deputy director at the state water board’s division of drinking water. The effort will take about two years.
Solano County — home to large pastures about an hour northeast of San Francisco — tested soil where biosolids had been applied to its fields, most of which came from the Bay Area. In preliminary results, consultants found PFAS at every location, including places where biosolids had historically not been applied. In recent years, landowners expressed reservations about the county’s biosolids program, and in 2024 no farms participated in the practice, said Trey Strickland, manager of the environmental health services division.
“It was probably a ‘not in my backyard’ kind of thing,” Strickland said. “Spread the poop somewhere else, away from us.”
Los Angeles County, meanwhile, hauls much of its biosolids to Kern County or out of state. Green Acres, a farm near Bakersfield and owned by the city of Los Angeles, has applied as much as 80,000 dry tons of biosolids annually, fertilizing crops for animal feed like corn and wheat. Concerned about the environmental and health implications, for more than a decade Kern County fought the practice until the legal battle ended in 2017. At the time, Dean Florez, a former state senator, told the Los Angeles Times that “it’s been a David and Goliath battle from Day One.”
“We probably won’t know the effects of this for many years,” he added. “We do know one thing: If it was healthy and OK, L.A. would do it in L.A. County.”